Articles:
ethylamine
Notes:
Found in foods and drinks
Ethylamine is an organic compound with the formula CH3CH2NH2. This colourless gas has a strong ammonia-like odor. Ethylamine is widely used in chemical industry and organic synthesis. (Wikipedia)
| CAS Number: | 75-04-7 | 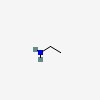 3D/inchi 3D/inchi
|
| ECHA EINECS - REACH Pre-Reg: | 200-834-7 | |
| FDA UNII: | YG6MGA6AT5 | |
| Nikkaji Web: | J1.437K | |
| Beilstein Number: | 0505933 | |
| MDL: | MFCD00008160 | |
| CoE Number: | 10477 | |
| XlogP3-AA: | -0.30 (est) | |
| Molecular Weight: | 45.08479000 | |
| Formula: | C2 H7 N | |
| NMR Predictor: | Predict (works with chrome, Edge or firefox) | |
Category: flavoring agents
US / EU / FDA / JECFA / FEMA / FLAVIS / Scholar / Patent Information:
| Google Scholar: | Search |
| Google Books: | Search |
| Google Scholar: with word "volatile" | Search |
| Google Scholar: with word "flavor" | Search |
| Google Scholar: with word "odor" | Search |
| Perfumer and Flavorist: | Search |
| Google Patents: | Search |
| US Patents: | Search |
| EU Patents: | Search |
| Pubchem Patents: | Search |
| PubMed: | Search |
| NCBI: | Search |
| JECFA Food Flavoring: | 1579 ethylamine |
| DG SANTE Food Flavourings: | 11.015 ethylamine |
| FEMA Number: | 4236 ethylamine |
| FDA: | No longer provide for the use of these seven synthetic flavoring substances |
| FDA Mainterm (SATF): | 75-04-7 ; ETHYLAMINE |
Physical Properties:
| Appearance: | colorless to yellow gas (est) |
| Assay: | 95.00 to 100.00 % |
| Food Chemicals Codex Listed: | No |
| Specific Gravity: | 0.68200 to 0.68600 @ 25.00 °C. |
| Pounds per Gallon - (est).: | 5.675 to 5.708 |
| Melting Point: | -81.00 to -80.00 °C. @ 760.00 mm Hg |
| Boiling Point: | 16.00 to 17.00 °C. @ 760.00 mm Hg |
| Vapor Pressure: | 1132.333008 mmHg @ 25.00 °C. (est) |
| Flash Point: | 1.00 °F. TCC ( -17.22 °C. ) |
| logP (o/w): | -0.130 |
| Soluble in: | |
| propylene glycol | |
| water, 1e+006 mg/L @ 25 °C (est) | |
| water, 1.00E+06 mg/L @ 25 °C (exp) | |
Organoleptic Properties:
| Odor Type: ammoniacal | |
| ammoniacal fishy | |
| Odor Description: at 0.01 % in propylene glycol. | ammonia fishy Luebke, William tgsc, (1998) |
| Odor and/or flavor descriptions from others (if found). | |
Cosmetic Information:
| None found |
Suppliers:
| BASF |
| Ethylamine |
| Eastman Chemical |
| Monoethylamine 70% |
| EMD Millipore |
| For experimental / research use only. |
| Ethylamine (70% solution in water) |
| Penta International |
| ETHYLAMINE 70% SOLUTION IN WATER |
| Shiva Chemicals and Pharmaceuticals |
| Ethyl Amine |
| Sigma-Aldrich: Aldrich |
| For experimental / research use only. |
| Ethylamine 99.0% |
| Silver Fern Chemical |
| Ethylamine
Odor: characteristic Use: Ethylamine can be used as a dye intermediate, a solvent extractor, for refining petroleum, as a stabilizer in rubbers and detergents, and organic synthesis. |
| Taminco (Eastman) |
| monoethylamine |
| TCI AMERICA |
| For experimental / research use only. |
| Ethylamine (ca. 70% in Water, ca. 12mol/L) |
Safety Information:
| Preferred SDS: View | |
| European information : | |
| Most important hazard(s): | |
| Xi - Irritant | |
|
R 11 - Highly flammable. R 36/37 - Irritating to eyes and respiratory system. S 02 - Keep out of the reach of children. S 16 - Keep away from sources of ignition - No Smoking. S 20/21 - When using do not eat, drink or smoke. S 23 - Do not breath vapour. S 24/25 - Avoid contact with skin and eyes. S 26 - In case of contact with eyes, rinse immediately with plenty of water and seek medical advice. S 33 - Take precautionary measures against static discharge. S 36/37/39 - Wear suitable clothing, gloves and eye/face protection. | |
| Hazards identification | |
| Classification of the substance or mixture | |
| GHS Classification in accordance with 29 CFR 1910 (OSHA HCS) | |
| None found. | |
| GHS Label elements, including precautionary statements | |
| Pictogram | |
| Hazard statement(s) | |
| None found. | |
| Precautionary statement(s) | |
| None found. | |
| Oral/Parenteral Toxicity: | |
|
intravenous-rabbit LDLo 350 mg/kg "Abdernalden's Handbuch der Biologischen Arbeitsmethoden." Vol. 4, Pg. 1295, 1935. oral-rat LD50 400 mg/kg AMA Archives of Industrial Hygiene and Occupational Medicine. Vol. 10, Pg. 61, 1954. | |
| Dermal Toxicity: | |
|
skin-rabbit LD50 390 uL/kg AMA Archives of Industrial Hygiene and Occupational Medicine. Vol. 10, Pg. 61, 1954. | |
| Inhalation Toxicity: | |
|
inhalation-mammal (species unspecified) LC50 2300 mg/m3 Toksikologiya Novykh Promyshlennykh Khimicheskikh Veshchestv. Toxicology of New Industrial Chemical Substances. For English translation, see TNICS*. Vol. 14, Pg. 80, 1975. inhalation-rat LC50 5540 ppm/1H SENSE ORGANS AND SPECIAL SENSES: CORNEAL DAMAGE: EYE LUNGS, THORAX, OR RESPIRATION: DYSPNEA National Technical Information Service. Vol. OTS0538173 | |
Safety in Use Information:
| Category: | flavoring agents | ||
| Recommendation for ethyl amine usage levels up to: | |||
| not for fragrance use. | |||
| Maximised Survey-derived Daily Intakes (MSDI-EU): | 0.012 (μg/capita/day) | ||
| Maximised Survey-derived Daily Intakes (MSDI-USA): | 0.20 (μg/capita/day) | ||
| Modified Theoretical Added Maximum Daily Intake (mTAMDI): | 340 (μg/person/day) | ||
| Threshold of Concern: | 1800 (μg/person/day) | ||
| Structure Class: | I | ||
| Use levels for FEMA GRAS flavoring substances on which the FEMA Expert Panel based its judgments that the substances are generally recognized as safe (GRAS). | |||
| The Expert Panel also publishes separate extensive reviews of scientific information on all FEMA GRAS flavoring substances and can be found at FEMA Flavor Ingredient Library | |||
| publication number: 22 | |||
| Click here to view publication 22 | |||
| average usual ppm | average maximum ppm | ||
| baked goods: | 2.00000 | 10.00000 | |
| beverages(nonalcoholic): | - | - | |
| beverages(alcoholic): | - | - | |
| breakfast cereal: | 0.20000 | 1.00000 | |
| cheese: | 0.40000 | 2.00000 | |
| chewing gum: | - | - | |
| condiments / relishes: | 0.10000 | 0.50000 | |
| confectionery froastings: | 1.00000 | 5.00000 | |
| egg products: | - | - | |
| fats / oils: | 0.10000 | 0.50000 | |
| fish products: | 0.20000 | 1.00000 | |
| frozen dairy: | 0.40000 | 2.00000 | |
| fruit ices: | 0.40000 | 2.00000 | |
| gelatins / puddings: | - | - | |
| granulated sugar: | - | - | |
| gravies: | 0.10000 | 0.50000 | |
| hard candy: | - | - | |
| imitation dairy: | - | - | |
| instant coffee / tea: | - | - | |
| jams / jellies: | - | - | |
| meat products: | 0.20000 | 1.00000 | |
| milk products: | 0.40000 | 2.00000 | |
| nut products: | - | - | |
| other grains: | 0.20000 | 1.00000 | |
| poultry: | 0.20000 | 1.00000 | |
| processed fruits: | 0.40000 | 2.00000 | |
| processed vegetables: | - | - | |
| reconstituted vegetables: | - | - | |
| seasonings / flavors: | 0.10000 | 0.50000 | |
| snack foods: | 1.00000 | 5.00000 | |
| soft candy: | - | - | |
| soups: | 0.10000 | 0.50000 | |
| sugar substitutes: | - | - | |
| sweet sauces: | - | - | |
| Food categories according to Commission Regulation EC No. 1565/2000 (EC, 2000) in FGE.06 (EFSA, 2002a). According to the Industry the "normal" use is defined as the average of reported usages and "maximum use" is defined as the 95th percentile of reported usages (EFSA, 2002i). | |||
| Note: mg/kg = 0.001/1000 = 0.000001 = 1/1000000 = ppm. | |||
| average usage mg/kg | maximum usage mg/kg | ||
| Dairy products, excluding products of category 02.0 (01.0): | 0.40000 | 2.00000 | |
| Fats and oils, and fat emulsions (type water-in-oil) (02.0): | 0.10000 | 0.50000 | |
| Edible ices, including sherbet and sorbet (03.0): | 0.40000 | 2.00000 | |
| Processed fruit (04.1): | 0.40000 | 2.00000 | |
| Processed vegetables (incl. mushrooms & fungi, roots & tubers, pulses and legumes), and nuts & seeds (04.2): | - | - | |
| Confectionery (05.0): | 1.00000 | 5.00000 | |
| Chewing gum (05.0): | - | - | |
| Cereals and cereal products, incl. flours & starches from roots & tubers, pulses & legumes, excluding bakery (06.0): | 0.20000 | 1.00000 | |
| Bakery wares (07.0): | 2.00000 | 10.00000 | |
| Meat and meat products, including poultry and game (08.0): | 0.20000 | 1.00000 | |
| Fish and fish products, including molluscs, crustaceans and echinoderms (MCE) (09.0): | 0.20000 | 1.00000 | |
| Eggs and egg products (10.0): | - | - | |
| Sweeteners, including honey (11.0): | - | - | |
| Salts, spices, soups, sauces, salads, protein products, etc. (12.0): | 0.10000 | 0.50000 | |
| Foodstuffs intended for particular nutritional uses (13.0): | 0.20000 | 1.00000 | |
| Non-alcoholic ("soft") beverages, excl. dairy products (14.1): | - | - | |
| Alcoholic beverages, incl. alcohol-free and low-alcoholic counterparts (14.2): | 1.00000 | 5.00000 | |
| Ready-to-eat savouries (15.0): | 1.00000 | 5.00000 | |
| Composite foods (e.g. casseroles, meat pies, mincemeat) - foods that could not be placed in categories 01.0 - 15.0 (16.0): | 0.20000 | 1.00000 | |
Safety References:
| European Food Safety Athority(EFSA): | Flavor usage levels; Subacute, Subchronic, Chronic and Carcinogenicity Studies; Developmental / Reproductive Toxicity Studies; Genotoxicity Studies... |
| European Food Safety Authority (EFSA) reference(s): | |
| Flavouring Group Evaluation 86, (FGE.86)[1] - Consideration of aliphatic and aromatic amines and amides evaluated by JECFA (65th meeting) - Scientific Opinion of the Panel on Food Additives - Flavourings, Processing Aids and Materials in Contact with Food View page or View pdf | |
| Scientific Opinion on Flavouring Group Evaluation 86, Revision 1 (FGE.86Rev1): Consideration of aliphatic and aromatic amines and amides evaluated by JECFA (65th meeting) View page or View pdf | |
| Scientific Opinion on Flavouring Group Evaluation 86, Revision 2 (FGE.86Rev2): Consideration of aliphatic and arylalkyl amines and amides evaluated by JECFA (65th meeting) View page or View pdf | |
| EPI System: | View |
| NIOSH International Chemical Safety Cards: | search |
| NIOSH Pocket Guide: | search |
| Chemical Carcinogenesis Research Information System: | Search |
| AIDS Citations: | Search |
| Cancer Citations: | Search |
| Toxicology Citations: | Search |
| EPA Substance Registry Services (TSCA): | 75-04-7 |
| EPA ACToR: | Toxicology Data |
| EPA Substance Registry Services (SRS): | Registry |
| Laboratory Chemical Safety Summary : | 6341 |
| National Institute of Allergy and Infectious Diseases: | Data |
| WISER: | UN 2270 |
| WGK Germany: | 1 |
| ethanamine | |
| Chemidplus: | 0000075047 |
| EPA/NOAA CAMEO: | hazardous materials |
| RTECS: | 75-04-7 |
References:
| ethanamine | |
| NIST Chemistry WebBook: | Search Inchi |
| Canada Domestic Sub. List: | 75-04-7 |
| Pubchem (cid): | 6341 |
| Pubchem (sid): | 134970734 |
| Pherobase: | View |
Other Information:
| (IUPAC): | Atomic Weights of the Elements 2011 (pdf) |
| Videos: | The Periodic Table of Videos |
| tgsc: | Atomic Weights use for this web site |
| (IUPAC): | Periodic Table of the Elements |
| FDA Substances Added to Food (formerly EAFUS): | View |
| CHEBI: | View |
| CHEMBL: | View |
| UM BBD: | Search |
| KEGG (GenomeNet): | C00797 |
| HMDB (The Human Metabolome Database): | HMDB13231 |
| FooDB: | FDB003242 |
| Export Tariff Code: | 2921.19.1100 |
| VCF-Online: | VCF Volatile Compounds in Food |
| ChemSpider: | View |
| Wikipedia: | View |
| Formulations/Preparations: •grades: technical (anhydrous and 70% aq soln); pure, 98.5% minimum. •available commercially as 50% or 70% aqueous solutions | |
Potential Blenders and core components note
| None Found | ||
Potential Uses:
| None Found |
Occurrence (nature, food, other): note
| apple fruit Search Trop Picture | |
| banana fruit Search Trop Picture | |
| barley seed Search Trop Picture | |
| cabbage leaf Search Trop Picture | |
| carrot root Search Trop Picture | |
| corn seed Search Trop Picture | |
| corn sprout Search Trop Picture | |
| elder black elder flower Search Trop Picture | |
| grape fruit juice Search Trop Picture | |
| soybean seed Search Trop Picture | |
| spinach leaf Search Trop Picture |
Synonyms:
| aminoethane | |
| 1- | aminoethane |
| ethanamine | |
| mono | ethyl amine |
| N- | ethyl amine |
| ethylamine | |
| mono | ethylamine |

