|
Category: natural substances and extractives
US / EU / FDA / JECFA / FEMA / FLAVIS / Scholar / Patent Information:
Physical Properties:
| Appearance: | pale yellow to yellow clear oily liquid (est) |
| Assay: | 92.00 to 100.00 %
|
| Food Chemicals Codex Listed: | No |
| Boiling Point: | 427.00 to 428.00 °C. @ 760.00 mm Hg
|
| Flash Point: | 302.00 °F. TCC ( 150.00 °C. )
|
| logP (o/w): | 3.789 (est) |
| Soluble in: |
| | water, 3.378 mg/L @ 25 °C (est) |
| Insoluble in: |
| | paraffin oil |
Organoleptic Properties:
| |
| Odor and/or flavor descriptions from others (if found). |
| |
| |
Cosmetic Information:
Suppliers:
Safety Information:
| Preferred SDS: View |
| |
| Hazards identification |
| |
| Classification of the substance or mixture |
| GHS Classification in accordance with 29 CFR 1910 (OSHA HCS) |
| None found. |
| GHS Label elements, including precautionary statements |
| |
| Pictogram | |
| |
| Hazard statement(s) |
| None found. |
| Precautionary statement(s) |
| None found. |
| Oral/Parenteral Toxicity: |
oral-mouse LD50 687 mg/kg
Journal of Pharmacobio-Dynamics. Vol. 7, Pg. 836, 1984.
intraperitoneal-mouse LD50 109 mg/kg
Journal of Pharmacobio-Dynamics. Vol. 7, Pg. 836, 1984.
intravenous-mouse LD50 50900 ug/kg
Journal of Pharmacobio-Dynamics. Vol. 7, Pg. 836, 1984.
|
| Dermal Toxicity: |
|
Not determined
|
| Inhalation Toxicity: |
|
Not determined
|
Safety in Use Information:
| Category: | natural substances and extractives |
| Recommendation for 6-shogaol usage levels up to: | | | not for fragrance use.
|
| |
| Recommendation for 6-shogaol flavor usage levels up to: |
| | not for flavor use.
|
Safety References:
References:
Other Information:
Potential Blenders and core components notePotential Uses:
Occurrence (nature, food, other): noteSynonyms:
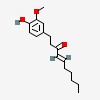
| 4- | decen-3-one, 1-(4-hydroxy-3-methoxyphenyl)-, (4E)- | | (E)-1-(4- | hydroxy-3-methoxy-phenyl)-dec-4-en-3-one | | (E)-1-(4- | hydroxy-3-methoxy-phenyl)dec-4-en-3-one | | 1-(4- | hydroxy-3-methoxyphenyl)-4-decen-3-one | | (4E)-1-(4- | hydroxy-3-methoxyphenyl)dec-4-en-3-one | | (E)-1-(4- | hydroxy-3-methoxyphenyl)dec-4-en-3-one | | (6)- | shogaol | | (E)- | shogaol | | [6]- | shogaol |
Articles:
| PubMed: | Cytotoxic activity against small cell lung cancer cell line and chromatographic fingerprinting of six isolated compounds from the ethanolic extract of Benjakul. |
| PubMed: | Anti-inflammatory activity of grains of paradise (Aframomum melegueta Schum) extract. |
| PubMed: | Modulation of cytochrome P450 metabolism and transport across intestinal epithelial barrier by ginger biophenolics. |
| PubMed: | Ginger compound [6]-shogaol and its cysteine-conjugated metabolite (M2) activate Nrf2 in colon epithelial cells in vitro and in vivo. |
| PubMed: | Anthelmintic constituents from ginger (Zingiber officinale) against Hymenolepis nana. |
| PubMed: | [6]-Shogaol inhibits α-MSH-induced melanogenesis through the acceleration of ERK and PI3K/Akt-mediated MITF degradation. |
| PubMed: | Influence of side chain structure changes on antioxidant potency of the [6]-gingerol related compounds. |
| PubMed: | 6-Shogaol exerts anti-proliferative and pro-apoptotic effects through the modulation of STAT3 and MAPKs signaling pathways. |
| PubMed: | 6-shogaol, a major compound in ginger, induces aryl hydrocarbon receptor-mediated transcriptional activity and gene expression. |
| PubMed: | 6-Shogaol, an active constituent of ginger, attenuates neuroinflammation and cognitive deficits in animal models of dementia. |
| PubMed: | Cysteine-conjugated metabolites of ginger components, shogaols, induce apoptosis through oxidative stress-mediated p53 pathway in human colon cancer cells. |
| PubMed: | Synthesis and quorum sensing inhibitory activity of key phenolic compounds of ginger and their derivatives. |
| PubMed: | Ginger and its pungent constituents non-competitively inhibit serotonin currents on visceral afferent neurons. |
| PubMed: | 6-Shogaol from dried ginger inhibits growth of prostate cancer cells both in vitro and in vivo through inhibition of STAT3 and NF-κB signaling. |
| PubMed: | Variations in the contents of gingerols and chromatographic fingerprints of ginger root extracts prepared by different preparation methods. |
| PubMed: | Role of 6-shogaol in tert -butyl hydroperoxide-induced apoptosis of HepG2 cells. |
| PubMed: | Reply to Comments on the article "[6]-Shogaol induced calcium signal in rat insulinoma cells". |
| PubMed: | Comments on the article "[6]-Shogaol induced calcium signal in rat insulinoma cells". |
| PubMed: | Multitargeted effects of hangeshashinto for treatment of chemotherapy-induced oral mucositis on inducible prostaglandin E2 production in human oral keratinocytes. |
| PubMed: | Induction of lung cancer cell apoptosis through a p53 pathway by [6]-shogaol and its cysteine-conjugated metabolite M2. |
| PubMed: | Enterohepatic recirculation of bioactive ginger phytochemicals is associated with enhanced tumor growth-inhibitory activity of ginger extract. |
| PubMed: | Antitumor activity of gemcitabine can be potentiated in pancreatic cancer through modulation of TLR4/NF-κB signaling by 6-shogaol. |
| PubMed: | [6]-shogaol induces Ca²⁺ signals by activating the TRPV1 channels in the rat insulinoma INS-1E cells. |
| PubMed: | Inhibition of human low-density lipoprotein oxidation in vitro by ginger extracts. |
| PubMed: | Preventive Effect of TU-100 on a Type-2 Model of Colitis in Mice: Possible Involvement of Enhancing Adrenomedullin in Intestinal Epithelial Cells. |
| PubMed: | [6]-shogaol inhibits growth and induces apoptosis of non-small cell lung cancer cells by directly regulating Akt1/2. |
| PubMed: | 6-Shogaol induces apoptosis in human leukemia cells through a process involving caspase-mediated cleavage of eIF2α. |
| PubMed: | 6-Shogaol inhibits chondrocytes' innate immune responses and cathepsin-K activity. |
| PubMed: | Active components of ginger potentiate β-agonist-induced relaxation of airway smooth muscle by modulating cytoskeletal regulatory proteins. |
| PubMed: | A novel shogaol analog suppresses cancer cell invasion and inflammation, and displays cytoprotective effects through modulation of NF-κB and Nrf2-Keap1 signaling pathways. |
| PubMed: | 6-Shogaol, an active compound of ginger, protects dopaminergic neurons in Parkinson's disease models via anti-neuroinflammation. |
| PubMed: | Cysteine-conjugated metabolite of ginger component [6]-shogaol serves as a carrier of [6]-shogaol in cancer cells and in mice. |
| PubMed: | 6-Shogaol inhibits breast and colon cancer cell proliferation through activation of peroxisomal proliferator activated receptor γ (PPARγ). |
| PubMed: | [6]-Shogaol inhibits the production of proinflammatory cytokines via regulation of NF-κB and phosphorylation of JNK in HMC-1 cells. |
| PubMed: | Glutathione conjugation attenuates biological activities of 6-dehydroshogaol from ginger. |
| PubMed: | Population pharmacokinetic analysis of daikenchuto, a traditional Japanese medicine (Kampo) in Japanese and US health volunteers. |
| PubMed: | 6-Shogaol Protects against Oxidized LDL-Induced Endothelial Injruries by Inhibiting Oxidized LDL-Evoked LOX-1 Signaling. |
| PubMed: | Ginger and its pungent constituents non-competitively inhibit activation of human recombinant and native 5-HT3 receptors of enteric neurons. |
| PubMed: | Highly efficient sample preparation and quantification of constituents from traditional Chinese herbal medicines using matrix solid-phase dispersion extraction and UPLC-MS/MS. |
| PubMed: | Role of the Toll Like receptor (TLR) radical cycle in chronic inflammation: possible treatments targeting the TLR4 pathway. |
| PubMed: | A new phenanthrene derivative and two diarylheptanoids from the roots of Brassica rapa ssp. campestris inhibit the growth of cancer cell lines and LDL-oxidation. |
| PubMed: | Invadopodia-associated proteins blockade as a novel mechanism for 6-shogaol and pterostilbene to reduce breast cancer cell motility and invasion. |
| PubMed: | [6]-shogaol attenuates neuronal apoptosis in hydrogen peroxide-treated astrocytes through the up-regulation of neurotrophic factors. |
| PubMed: | Metabolites of ginger component [6]-shogaol remain bioactive in cancer cells and have low toxicity in normal cells: chemical synthesis and biological evaluation. |
| PubMed: | Metabolism of ginger component [6]-shogaol in liver microsomes from mouse, rat, dog, monkey, and human. |
| PubMed: | Characterization of thiol-conjugated metabolites of ginger components shogaols in mouse and human urine and modulation of the glutathione levels in cancer cells by [6]-shogaol. |
| PubMed: | Grains of paradise (Aframomum melegueta) extract activates brown adipose tissue and increases whole-body energy expenditure in men. |
| PubMed: | Epithelial transient receptor potential ankyrin 1 (TRPA1)-dependent adrenomedullin upregulates blood flow in rat small intestine. |
| PubMed: | The Cytotoxicity Mechanism of 6-Shogaol-Treated HeLa Human Cervical Cancer Cells Revealed by Label-Free Shotgun Proteomics and Bioinformatics Analysis. |
| PubMed: | Simultaneous determination of gingerols and shogaol using capillary liquid chromatography and its application in discrimination of three ginger varieties from Indonesia. |
| PubMed: | [Effect of Zingiber offiicinale and Aconitum cainichaeli before and after compatibility on contents of four gingerols]. |
| PubMed: | [6]-Shogaol inhibits melanogenesis in B16 mouse melanoma cells through activation of the ERK pathway. |
| PubMed: | Effects of ginger and its constituents on airway smooth muscle relaxation and calcium regulation. |
| PubMed: | Identification of phase II metabolites of thiol-conjugated [6]-shogaol in mouse urine using high-performance liquid chromatography tandem mass spectrometry. |
| PubMed: | In vitro antioxidant and anti-inflammatory activities of 1-dehydro-[6]-gingerdione, 6-shogaol, 6-dehydroshogaol and hexahydrocurcumin. |
| PubMed: | Anti-platelet aggregation and vasorelaxing effects of the constituents of the rhizomes of Zingiber officinale. |
| PubMed: | 6-Shogaol induces apoptosis in human hepatocellular carcinoma cells and exhibits anti-tumor activity in vivo through endoplasmic reticulum stress. |
| PubMed: | 6-shogaol-rich extract from ginger up-regulates the antioxidant defense systems in cells and mice. |
| PubMed: | Molecular mechanism inhibiting human hepatocarcinoma cell invasion by 6-shogaol and 6-gingerol. |
| PubMed: | Optimization of Extraction Conditions for the 6-Shogaol-rich Extract from Ginger (Zingiber officinale Roscoe). |
| PubMed: | Zingiber officinale (ginger) as an anti-emetic in cancer chemotherapy: a review. |
| PubMed: | Anti-Candida and radical scavenging activities of essential oils and oleoresins of Zingiber officinale Roscoe and essential oils of other plants belonging to the family Zingiberaceae. |
| PubMed: | 6-Shogaol, a ginger product, modulates neuroinflammation: a new approach to neuroprotection. |
| PubMed: | Effects of [6]-shogaol on cholinergic signaling in HT22 cells following neuronal damage induced by hydrogen peroxide. |
| PubMed: | Phenylpropanoid ester from Zingiber officinale and their inhibitory effects on the production of nitric oxide. |
| PubMed: | [Phenolic and amide constituents from Lycianthes marlipoensis]. |
| PubMed: | Cytotoxic, cytoprotective and antioxidant effects of isolated phenolic compounds from fresh ginger. |
| PubMed: | Metabolism of [6]-shogaol in mice and in cancer cells. |
| PubMed: | Protection by [6]-shogaol against lipopolysaccharide-induced toxicity in murine astrocytes is related to production of brain-derived neurotrophic factor. |
| PubMed: | Anti-inflammatory effects of [6]-shogaol: potential roles of HDAC inhibition and HSP70 induction. |
| PubMed: | Pharmacokinetics of daikenchuto, a traditional Japanese medicine (kampo) after single oral administration to healthy Japanese volunteers. |
| PubMed: | Antiinflammatory effects of ginger and some of its components in human bronchial epithelial (BEAS-2B) cells. |
| PubMed: | Examination of the pharmacokinetics of active ingredients of ginger in humans. |
| PubMed: | Shogaols at proapoptotic concentrations induce G(2)/M arrest and aberrant mitotic cell death associated with tubulin aggregation. |
| PubMed: | Chemopreventive effects of dietary phytochemicals against cancer invasion and metastasis: phenolic acids, monophenol, polyphenol, and their derivatives. |
| PubMed: | Ginger suppresses phthalate ester-induced airway remodeling. |
| PubMed: | Protective Effects of Ginger against Aspirin-Induced Gastric Ulcers in Rats. |
| PubMed: | Effects of ginger constituents on the gastrointestinal tract: role of cholinergic M3 and serotonergic 5-HT3 and 5-HT4 receptors. |
| PubMed: | Preparation of the monomers of gingerols and 6-shogaol by flash high speed counter-current chromatography. |
| PubMed: | Quantitation of 6-, 8- and 10-Gingerols and 6-Shogaol in Human Plasma by High-Performance Liquid Chromatography with Electrochemical Detection. |
| PubMed: | 6-Shogaol, an active constituent of ginger, inhibits breast cancer cell invasion by reducing matrix metalloproteinase-9 expression via blockade of nuclear factor-κB activation. |
| PubMed: | Profiling of the compounds absorbed in human plasma and urine after oral administration of a traditional Japanese (kampo) medicine, daikenchuto. |
| PubMed: | Effect of [6]-shogaol on cytosolic Ca2+ levels and proliferation in human oral cancer cells (OC2). |
| PubMed: | Zingiber officinale (ginger) compounds have tetracycline-resistance modifying effects against clinical extensively drug-resistant Acinetobacter baumannii. |
| PubMed: | Larvicidal constituents of Zingiber officinale (ginger) against Anisakis simplex. |
| PubMed: | Anti-invasion effects of 6-shogaol and 6-gingerol, two active components in ginger, on human hepatocarcinoma cells. |
| PubMed: | [Chemical constituents of rhizomes of Zingiber officinale]. |
| PubMed: | 6-Shogaol is more effective than 6-gingerol and curcumin in inhibiting 12-O-tetradecanoylphorbol 13-acetate-induced tumor promotion in mice. |
| PubMed: | Pharmacokinetics of [6]-shogaol, a pungent ingredient of Zingiber officinale Roscoe (Part I). |
| PubMed: | Anti-inflammatory properties of red ginger (Zingiber officinale var. Rubra) extract and suppression of nitric oxide production by its constituents. |
| PubMed: | Six-shogaol inhibits production of tumour necrosis factor alpha, interleukin-1 beta and nitric oxide from lipopolysaccharide-stimulated RAW 264.7 macrophages. |
| PubMed: | Larvicidal activities of ginger (Zingiber officinale) against Angiostrongylus cantonensis. |
| PubMed: | Increased growth inhibitory effects on human cancer cells and anti-inflammatory potency of shogaols from Zingiber officinale relative to gingerols. |
| PubMed: | Comparative antioxidant and anti-inflammatory effects of [6]-gingerol, [8]-gingerol, [10]-gingerol and [6]-shogaol. |
| PubMed: | 6-Shogaol inhibits monosodium urate crystal-induced inflammation--an in vivo and in vitro study. |
| PubMed: | Identification and quantification of gingerols and related compounds in ginger dietary supplements using high-performance liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry. |
| PubMed: | 6-Shogaol, an active constituent of dietary ginger, induces autophagy by inhibiting the AKT/mTOR pathway in human non-small cell lung cancer A549 cells. |
| PubMed: | Compounds from Sichuan and Melegueta peppers activate, covalently and non-covalently, TRPA1 and TRPV1 channels. |
| PubMed: | TBK1-targeted suppression of TRIF-dependent signaling pathway of Toll-like receptors by 6-shogaol, an active component of ginger. |
| PubMed: | Inhibition of homodimerization of toll-like receptor 4 by 6-shogaol. |
| PubMed: | [Analysis of volatile and non-volatile compositions in ginger oleoresin by gas chromatography-mass spectrometry]. |
| PubMed: | Simultaneous determination of 6-gingerol, 8-gingerol, 10-gingerol and 6-shogaol in rat plasma by liquid chromatography-mass spectrometry: Application to pharmacokinetics. |
| PubMed: | Modulation of macrophage functions by compounds isolated from Zingiber officinale. |
| PubMed: | Specific reaction of alpha,beta-unsaturated carbonyl compounds such as 6-shogaol with sulfhydryl groups in tubulin leading to microtubule damage. |
| PubMed: | Goshuyuto, a traditional Japanese medicine for migraine, inhibits platelet aggregation in guinea-pig whole blood. |
| PubMed: | Analysis of anti-platelet aggregation components of Rhizoma Zingiberis using chicken thrombocyte extract and high performance liquid chromatography. |
| PubMed: | Pharmacokinetics of 6-gingerol, 8-gingerol, 10-gingerol, and 6-shogaol and conjugate metabolites in healthy human subjects. |
| PubMed: | 6-Shogaol suppressed lipopolysaccharide-induced up-expression of iNOS and COX-2 in murine macrophages. |
| PubMed: | [RP-HPLC fingerprint evaluating different ginger juice as processing material]. |
| PubMed: | 6-Shogaol and 6-gingerol, the pungent of ginger, inhibit TNF-alpha mediated downregulation of adiponectin expression via different mechanisms in 3T3-L1 adipocytes. |
| PubMed: | Changes in the contents of oleoresin and pungent bioactive principles of Jamaican ginger (Zingiber officinale Roscoe.) during maturation. |
| PubMed: | Cytotoxic components from the dried rhizomes of Zingiber officinale Roscoe. |
| PubMed: | 6-Shogaol induces apoptosis in human colorectal carcinoma cells via ROS production, caspase activation, and GADD 153 expression. |
| PubMed: | Ginger inhibits cell growth and modulates angiogenic factors in ovarian cancer cells. |
| PubMed: | Liquid chromatographic determination of 6-, 8-, 10-gingerol, and 6-shogaol in ginger (Zingiber officinale) as the raw herb and dried aqueous extract. |
| PubMed: | Stability of [6]-gingerol and [6]-shogaol in simulated gastric and intestinal fluids. |
| PubMed: | Ginger ingredients reduce viability of gastric cancer cells via distinct mechanisms. |
| PubMed: | High-performance liquid chromatographic analysis of 6-gingerol, 8-gingerol, 10-gingerol, and 6-shogaol in ginger-containing dietary supplements, spices, teas, and beverages. |
| PubMed: | 6-shogaol (alkanone from ginger) induces apoptotic cell death of human hepatoma p53 mutant Mahlavu subline via an oxidative stress-mediated caspase-dependent mechanism. |
| PubMed: | A nonpungent component of steamed ginger--[10]-shogaol--increases adrenaline secretion via the activation of TRPV1. |
| PubMed: | 6-Shogaol reduced chronic inflammatory response in the knees of rats treated with complete Freund's adjuvant. |
| PubMed: | 6-Shogaol, a natural product, reduces cell death and restores motor function in rat spinal cord injury. |
| PubMed: | Species differences in the prokinetic effects of ginger. |
| PubMed: | Variation in concentration and labeling of ginger root dietary supplements. |
| PubMed: | The effect of extracts from ginger rhizome on inflammatory mediator production. |
| PubMed: | Mode of action of gingerols and shogaols on 5-HT3 receptors: binding studies, cation uptake by the receptor channel and contraction of isolated guinea-pig ileum. |
| PubMed: | Cardiovascular effects of ginger aqueous extract and its phenolic constituents are mediated through multiple pathways. |
| PubMed: | 5-HT3 receptor blocking activity of arylalkanes isolated from the rhizome of Zingiber officinale. |
| PubMed: | Commercially processed dry ginger (Zingiber officinale): composition and effects on LPS-stimulated PGE2 production. |
| PubMed: | Separation and isolation methods for analysis of the active principles of Sho-saiko-to (SST) oriental medicine. |
| PubMed: | Component of Zingiber officinale that improves the enhancement of small intestinal transport. |
| PubMed: | The herbal medicine Dai-kenchu-to and one of its active components [6]-shogaol increase intestinal blood flow in rats. |
| PubMed: | The stability of gingerol and shogaol in aqueous solutions. |
| PubMed: | Stomachic principles in ginger. III. An anti-ulcer principle, 6-gingesulfonic acid, and three monoacyldigalactosylglycerols, gingerglycolipids A, B, and C, from Zingiberis Rhizoma originating in Taiwan. |
| PubMed: | Capsaicin-like effect of (6)-shogaol on substance P-containing primary afferents of rats: a possible mechanism of its analgesic action. |
| PubMed: | [Stomachic principles in ginger. II. Pungent and anti-ulcer effects of low polar constituents isolated from ginger, the dried rhizoma of Zingiber officinale Roscoe cultivated in Taiwan. The absolute stereostructure of a new diarylheptanoid]. |
| PubMed: | 6-Gingesulfonic acid, a new anti-ulcer principle, and gingerglycolipids A, B, and C, three new monoacyldigalactosylglycerols, from zingiberis rhizoma originating in Taiwan. |
| PubMed: | [The study of Chinese herbal medicinal prescription with enzyme inhibitory activity. V. The study of hange-shashin-to, kanzo-shashin-to, shokyo-shashin-to with adenosine 3',5'-cyclic monophosphate phosphodiesterase]. |
| PubMed: | [The effect of ginger on serotonin induced hypothermia and diarrhea]. |
| PubMed: | Gastrointestinal motility enhancing effect of ginger and its active constituents. |
| PubMed: | Lethal efficacy of extract from Zingiber officinale (traditional Chinese medicine) or [6]-shogaol and [6]-gingerol in Anisakis larvae in vitro. |
| PubMed: | Reversed effects between crude and processed ginger extracts on PGF2 alpha-induced contraction in mouse mesenteric veins. |
| PubMed: | Chemical structural requirement in gingerol derivatives for potentiation of prostaglandin F2 alpha-induced contraction in isolated mesenteric veins of mice. |
| PubMed: | [Pharmacological studies on ginger. V. Pharmacological comparison between (6)-shogaol and capsaicin]. |
| PubMed: | Pharmacological studies on ginger. II. Pressor action of (6)-shogaol in anesthetized rats, or hindquarters, tail and mesenteric vascular beds of rats. |
| PubMed: | [Pharmacological studies on ginger. IV. Effect of (6)-shogaol on the arachidonic cascade]. |
| PubMed: | Pharmacological studies on ginger. III. Effect of the spinal destruction on (6)-shogaol-induced pressor response in rats. |
| PubMed: | Pharmacological studies on ginger. I. Pharmacological actions of pungent constitutents, (6)-gingerol and (6)-shogaol. |
| PubMed: | The active part of the [6]-gingerol molecule in mutagenesis. |
|
 3D/inchi
3D/inchi
