Articles:
3,7-dimethylpurine-2,6-dione
Notes:
the principle alkaloid in theobroma cacao (the cacao bean) and other plants. a xanthine alkaloid that is used as a bronchodilator and as a vasodilator. it has a weaker diuretic activity than theophylline and is also a less powerful stimulant of smooth muscle. it has practically no stimulant effect on the central nervous system. it was formerly used as a diuretic and in the treatment of angina pectoris and hypertension. (from martindale, the extra pharmacopoeia, 30th ed, pp1318-9) Constit. of tea leaves (Camellia thea), cocoa Theobroma cacao, cola nut (Cola acuminata) and guarana (Paullinia cupana); flavouring ingredient with a bitter taste
3,7-Dimethylxanthine. The principle alkaloid in Theobroma cacao (the cacao bean) and other plants. A xanthine alkaloid that is used as a bronchodilator and as a vasodilator. It has a weaker diuretic activity than theophylline and is also a less powerful stimulant of smooth muscle. It has practically no stimulant effect on the central nervous system. It was formerly used as a diuretic and in the treatment of angina pectoris and hypertension. (From Martindale, The Extra Pharmacopoeia, 30th ed, pp1318-9) -- Pubchem; As a methylated xanthine, theobromine is a potent Cyclic adenosine monophosphate (cAMP) phosphodiesterase inhibitor; this means that it helps prevent the enzyme phosphodiesterase from converting the active cAMP to an inactive form. cAMP works as a second messenger in many hormone- and neurotransmitter-controlled metabolic systems, such as the breakdown of glycogen. When the inactivation of cAMP is inhibited by a compound such as theobromine, the effects of the neurotransmitter or hormone which stimulated the production of cAMP are much longer lived. The net result is generally a stimulatory effect.; As it is a myocardial stimulant as well as a vasodilator, it increases heartbeat, yet it also dilates blood vessels, causing a reduced blood pressure. However, a recent paper published suggested that the decrease in blood pressure may be caused by flavanols. Furthermore, its draining effect allows it to be used to treat cardiac failure, which can be caused by an excessive accumulation of fluid.; Even without dietary intake, theobromine may occur in the body as it is a product of the human metabolism of caffeine which is metabolised in the liver into 10% theobromine, 4% theophylline, and 80% paraxanthine.; In medicine, it is used as a diuretic, vasodilator, and myocardial stimulant. There is a possible association between prostate cancer and theobromine. -- Wikipedia; It is the primary alkaloid found in cocoa and chocolate, and is one of the causes for chocolate's mood-elevating effects. The amount found in chocolate is small enough that chocolate can be safely consumed by humans in large quantities, but animals that metabolize theobromine more slowly, such as cats and dogs, can easily consume enough chocolate to cause chocolate poisoning. -- Wikipedia; Theobromine is a bitter alkaloid of the methylxanthine family, which also includes the similar compounds theophylline and caffeine. Despite its name, the compound contains no bromine.Theobromine is derived from Theobroma, the genus of the cacao tree, which is composed of the Greek roots theo ("God") and broma ("food"), meaning "food of the gods". -- Wikipedia; Theobromine is a contributing factor in acid reflux because it relaxes the esophageal sphincter muscle, allowing stomach acid access to the esophagus. -- Wikipedia; Theobromine is a stimulant frequently confused with caffeine. Theobromine has very different effects on the human body from caffeine; Theobromine is a water insoluble, crystalline, bitter powder; the colour has been listed as either white or colourless. It has a similar, but lesser, effect to caffeine, making it a lesser homologue. Theobromine is an isomer of theophylline as well as paraxanthine. Theobromine is categorized as a dimethyl xanthine, which means it is a xanthine with two methyl groups.; Theobromine, also known as xantheose, is a bitter alkaloid of the cacao plant, found in chocolate, as well as in a number of chocolate-free foods made from theobromine sources including the leaves of the tea plant, the kola or cola nut, and acai berries[citation needed]. It is in the methylxanthine class of chemical compounds, which also includes the similar compounds theophylline and caffeine. (In caffeine, the only difference is that the NH group of theobromine is an N-CH3 group.) Despite its name, the compound contains no bromine ? theobromine is derived from Theobroma, the name of the genus of the cacao tree, (which itself is made up of the Greek roots theo ("God") and brosi ("food"), meaning "food of the gods") with the suffix -ine given to alkaloids and other basic nitrogen-containing compounds.; While theobromine and caffeine are similar in that they are related alkaloids, theobromine is weaker in both its inhibition of cyclic nucleotide phosphodiesterases and its antagonism of adenosine receptors. Therefore, theobromine has a lesser impact on the human central nervous system than caffeine. However, theobromine stimulates the heart to a greater degree.[citation needed] While theobromine is not as addictive, it has been cited as possibly causing addiction to chocolate. Theobromine has also been identified as one of the compounds contributing to chocolate's reputed role as an aphrodisiac.; it is a mild, lasting stimulant with a mood improving effect, whereas caffeine has a strong, immediate effect and increases stress. -- Wikipedia
| CAS Number: | 83-67-0 | 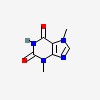 3D/inchi 3D/inchi
|
| ECHA EINECS - REACH Pre-Reg: | 201-494-2 | |
| FDA UNII: | OBD445WZ5P | |
| Nikkaji Web: | J3.874A | |
| Beilstein Number: | 0016464 | |
| MDL: | MFCD00022830 | |
| XlogP3: | -0.80 (est) | |
| Molecular Weight: | 180.16716000 | |
| Formula: | C7 H8 N4 O2 | |
| BioActivity Summary: | listing | |
| NMR Predictor: | Predict (works with chrome or firefox) | |
Category: flavoring agents
US / EU / FDA / JECFA / FEMA / FLAVIS / Scholar / Patent Information:
| Google Scholar: | Search |
| Google Books: | Search |
| Google Scholar: with word "volatile" | Search |
| Google Scholar: with word "flavor" | Search |
| Google Scholar: with word "odor" | Search |
| Perfumer and Flavorist: | Search |
| Google Patents: | Search |
| US Patents: | Search |
| EU Patents: | Search |
| Pubchem Patents: | Search |
| PubMed: | Search |
| NCBI: | Search |
| FDA/DG SANTE Petitions, Reviews, Notices: | |
| GRN 340 | Theobromine View - notice PDF |
| DG SANTE Food Flavourings: | 16.032 theobromine |
| FEMA Number: | 3591 theobromine |
| FDA: | No longer provide for the use of these seven synthetic flavoring substances |
| FDA Mainterm (SATF): | 83-67-0 ; THEOBROMINE |
Physical Properties:
| Appearance: | white powder (est) |
| Assay: | 98.00 to 100.00 % |
| Food Chemicals Codex Listed: | No |
| Melting Point: | 345.00 to 350.00 °C. @ 760.00 mm Hg |
| Flash Point: | 32.00 °F. TCC ( 0.00 °C. ) (est) |
| logP (o/w): | -0.780 |
| Shelf Life: | 24.00 month(s) or longer if stored properly. |
| Storage: | store in cool, dry place in tightly sealed containers, protected from heat and light. |
| Soluble in: | |
| alcohol | |
| water, 1.248e+004 mg/L @ 25 °C (est) | |
| water, 330 mg/L @ 25 °C (exp) | |
| Insoluble in: | |
| water | |
Organoleptic Properties:
| Flavor Type: bitter | |
| bitter | |
| Taste Description: | bitter |
| Odor and/or flavor descriptions from others (if found). | |
Cosmetic Information:
| CosIng: | cosmetic data |
| Cosmetic Uses: |
fragrance skin conditioning |
Suppliers:
| Alfa Biotechnology |
| For experimental / research use only. |
| Theobromine 98% |
| BOC Sciences |
| For experimental / research use only. |
| Theobromine >98% |
| Penta International |
| THEOBROMINE NATURAL 20% |
| Penta International |
| THEOBROMINE |
| Santa Cruz Biotechnology |
| For experimental / research use only. |
| Theobromine |
| Shaanxi Y-Herb Biotechnology |
| 10% 20% Theobromine Powder Natural Seed Polyphenols Alkalized Cocoa Bean Extract |
| Sigma-Aldrich: Sigma |
| For experimental / research use only. |
| Theobromine ≥99.0%, solid |
| TCI AMERICA |
| For experimental / research use only. |
| Theobromine >98.0%(HPLC)(T) |
Safety Information:
| Preferred SDS: View | |
| European information : | |
| Most important hazard(s): | |
| Xn - Harmful. | |
|
R 22 - Harmful if swallowed. S 02 - Keep out of the reach of children. S 20/21 - When using do not eat, drink or smoke. S 24/25 - Avoid contact with skin and eyes. S 26 - In case of contact with eyes, rinse immediately with plenty of water and seek medical advice. S 36 - Wear suitable protective clothing. | |
| Hazards identification | |
| Classification of the substance or mixture | |
| GHS Classification in accordance with 29 CFR 1910 (OSHA HCS) | |
| None found. | |
| GHS Label elements, including precautionary statements | |
| Pictogram | |
| Hazard statement(s) | |
| None found. | |
| Precautionary statement(s) | |
| None found. | |
| Oral/Parenteral Toxicity: | |
|
oral-rat LD50 1265 mg/kg Gigiena Truda i Professional'nye Zabolevaniya. Labor Hygiene and Occupational Diseases. Vol. 26(3), Pg. 59, 1982. oral-mouse LD50 837 mg/kg Gigiena Truda i Professional'nye Zabolevaniya. Labor Hygiene and Occupational Diseases. Vol. 26(3), Pg. 59, 1982. oral-human LDLo 26 mg/kg Journal of Pharmacology and Experimental Therapeutics. Vol. 86, Pg. 113, 1946. intraperitoneal-mouse LD50 552 mg/kg BEHAVIORAL: CONVULSIONS OR EFFECT ON SEIZURE THRESHOLD Acta Pharmaceutica Vol. 46, Pg. 93, 1996. oral-cat LD50 200 mg/kg "Prehled Prumyslove Toxikologie; Organicke Latky," Marhold, J., Prague, Czechoslovakia, Avicenum, 1986Vol. -, Pg. 1372, 1986. oral-dog LD50 300 mg/kg Toxicology and Applied Pharmacology. Vol. 53, Pg. 481, 1980. oral-human TDLo 26 mg/kg BEHAVIORAL: CHANGES IN MOTOR ACTIVITY (SPECIFIC ASSAY) GASTROINTESTINAL: NAUSEA OR VOMITING Journal of Pharmacology and Experimental Therapeutics. Vol. 86, Pg. 113, 1946. | |
| Dermal Toxicity: | |
|
subcutaneous-rabbit LDLo 1000 mg/kg "Abdernalden's Handbuch der Biologischen Arbeitsmethoden." Vol. 4, Pg. 1289, 1935. subcutaneous-mouse LD50 530 mg/kg Arzneimittel-Forschung. Drug Research. Vol. 6, Pg. 601, 1956. | |
| Inhalation Toxicity: | |
| Not determined | |
Safety in Use Information:
| Category: | flavoring agents | ||
| Recommendation for theobromine usage levels up to: | |||
| not for fragrance use. | |||
| Maximised Survey-derived Daily Intakes (MSDI-EU): | 30.00 (μg/capita/day) | ||
| Structure Class: | III | ||
| Use levels for FEMA GRAS flavoring substances on which the FEMA Expert Panel based its judgments that the substances are generally recognized as safe (GRAS). | |||
| The Expert Panel also publishes separate extensive reviews of scientific information on all FEMA GRAS flavoring substances and can be found at FEMA Flavor Ingredient Library | |||
| publication number: 11 | |||
| Click here to view publication 11 | |||
| average usual ppm | average maximum ppm | ||
| baked goods: | - | 1050.00000 | |
| beverages(nonalcoholic): | - | - | |
| beverages(alcoholic): | - | - | |
| breakfast cereal: | - | - | |
| cheese: | - | - | |
| chewing gum: | - | - | |
| condiments / relishes: | - | - | |
| confectionery froastings: | - | 4020.00000 | |
| egg products: | - | - | |
| fats / oils: | - | - | |
| fish products: | - | - | |
| frozen dairy: | - | - | |
| fruit ices: | - | - | |
| gelatins / puddings: | - | 795.00000 | |
| granulated sugar: | - | - | |
| gravies: | - | - | |
| hard candy: | - | - | |
| imitation dairy: | - | - | |
| instant coffee / tea: | - | - | |
| jams / jellies: | - | - | |
| meat products: | - | - | |
| milk products: | - | 990.00000 | |
| nut products: | - | - | |
| other grains: | - | - | |
| poultry: | - | - | |
| processed fruits: | - | - | |
| processed vegetables: | - | - | |
| reconstituted vegetables: | - | - | |
| seasonings / flavors: | - | - | |
| snack foods: | - | - | |
| soft candy: | - | 4020.00000 | |
| soups: | - | - | |
| sugar substitutes: | - | - | |
| sweet sauces: | - | 3300.00000 | |
| Food categories according to Commission Regulation EC No. 1565/2000 (EC, 2000) in FGE.06 (EFSA, 2002a). According to the Industry the "normal" use is defined as the average of reported usages and "maximum use" is defined as the 95th percentile of reported usages (EFSA, 2002i). | |||
| Note: mg/kg = 0.001/1000 = 0.000001 = 1/1000000 = ppm. | |||
| average usage mg/kg | maximum usage mg/kg | ||
| Dairy products, excluding products of category 02.0 (01.0): | 20.00000 | 70.00000 | |
| Fats and oils, and fat emulsions (type water-in-oil) (02.0): | - | - | |
| Edible ices, including sherbet and sorbet (03.0): | - | - | |
| Processed fruit (04.1): | - | - | |
| Processed vegetables (incl. mushrooms & fungi, roots & tubers, pulses and legumes), and nuts & seeds (04.2): | - | - | |
| Confectionery (05.0): | - | - | |
| Chewing gum (05.0): | - | - | |
| Cereals and cereal products, incl. flours & starches from roots & tubers, pulses & legumes, excluding bakery (06.0): | - | - | |
| Bakery wares (07.0): | - | - | |
| Meat and meat products, including poultry and game (08.0): | - | - | |
| Fish and fish products, including molluscs, crustaceans and echinoderms (MCE) (09.0): | - | - | |
| Eggs and egg products (10.0): | - | - | |
| Sweeteners, including honey (11.0): | - | - | |
| Salts, spices, soups, sauces, salads, protein products, etc. (12.0): | - | - | |
| Foodstuffs intended for particular nutritional uses (13.0): | - | - | |
| Non-alcoholic ("soft") beverages, excl. dairy products (14.1): | 75.00000 | 100.00000 | |
| Alcoholic beverages, incl. alcohol-free and low-alcoholic counterparts (14.2): | - | - | |
| Ready-to-eat savouries (15.0): | - | - | |
| Composite foods (e.g. casseroles, meat pies, mincemeat) - foods that could not be placed in categories 01.0 - 15.0 (16.0): | - | - | |
Safety References:
| European Food Safety Athority(EFSA): | Flavor usage levels; Subacute, Subchronic, Chronic and Carcinogenicity Studies; Developmental / Reproductive Toxicity Studies; Genotoxicity Studies... |
| European Food Safety Authority (EFSA) reference(s): | |
| Flavouring Group Evaluation 29 (FGE29)[1] - Substance from the priority list: Vinylbenzene from chemical group 31 - Scientific Opinion of the Panel on Food Additives, Flavourings, Processing Aids and Materials in Contact with Food (AFC) View page or View pdf | |
| Flavouring Group Evaluation 49, (FGE.49)[1]: Xanthin alkaloids from the Priority list from chemical group 30 View page or View pdf | |
| Scientific Opinion on Flavouring Group Evaluation 49, Revision 1 (FGE.49Rev1): xanthine alkaloids from the priority list View page or View pdf | |
| EPI System: | View |
| ClinicalTrials.gov: | search |
| Chemical Carcinogenesis Research Information System: | Search |
| AIDS Citations: | Search |
| Cancer Citations: | Search |
| Toxicology Citations: | Search |
| EPA GENetic TOXicology: | Search |
| EPA Substance Registry Services (TSCA): | 83-67-0 |
| EPA ACToR: | Toxicology Data |
| EPA Substance Registry Services (SRS): | Registry |
| Laboratory Chemical Safety Summary : | 5429 |
| National Institute of Allergy and Infectious Diseases: | Data |
| WGK Germany: | 1 |
| 3,7-dimethylpurine-2,6-dione | |
| Chemidplus: | 0000083670 |
| EPA/NOAA CAMEO: | hazardous materials |
| RTECS: | XH2275000 for cas# 83-67-0 |
References:
| 3,7-dimethylpurine-2,6-dione | |
| NIST Chemistry WebBook: | Search Inchi |
| Canada Domestic Sub. List: | 83-67-0 |
| Pubchem (cid): | 5429 |
| Pubchem (sid): | 134971694 |
Other Information:
| (IUPAC): | Atomic Weights of the Elements 2011 (pdf) |
| Videos: | The Periodic Table of Videos |
| tgsc: | Atomic Weights use for this web site |
| (IUPAC): | Periodic Table of the Elements |
| FDA Substances Added to Food (formerly EAFUS): | View |
| CHEBI: | View |
| CHEMBL: | View |
| Golm Metabolome Database: | Search |
| UM BBD: | Search |
| KEGG (GenomeNet): | C07480 |
| HMDB (The Human Metabolome Database): | HMDB02825 |
| FooDB: | FDB000455 |
| Export Tariff Code: | 2934.99.4400 |
| FDA Listing of Food Additive Status: | View |
| VCF-Online: | VCF Volatile Compounds in Food |
| ChemSpider: | View |
| Wikipedia: | View |
| Formulations/Preparations: •double salt or mixture of calcium theobromine and calcium salicylate. contains no less than 44% theobromine. white, amorphous powder. slightly saline taste. partly sol in water. aqueous solutions are alkaline to phenolphthalein. calcium salicyclate •equimolar mixture of sodium theobromine and sodium acetate, containing 1 h2o. theobromine 59.6%, anhydrous sodium acetate 27.1%. white, odorless or almost odorless, hygroscopic powder. absorbs co2 from the air becoming incompletely soluble. very soluble in water, sparingly soluble in cold alcohol; the solutions are strongly alkaline. sodium acetate •equimolar mixture of sodium theobromine and sodium salicylate, containing 1h2o. theobromine 47.3%, sodium salicylate 42.1%. white, odorless of almost odorless, hygroscopic powder. absorbs co2 from the air becoming incompletely soluble. soluble in 1 part water; slightly soluble in alcohol: the solutions are strongly alkaline. ph about 10. sodium salicylate | |
Potential Blenders and core components note
Potential Uses:
| None Found |
Occurrence (nature, food, other): note
| cacao bean Search Trop Picture | |
| cacao petiole Search Trop Picture | |
| cacao testa Search Trop Picture | |
| cocoa bean Search Trop Picture | |
| cocoa petiole Search Trop Picture | |
| coffee bean Search Trop Picture | |
| coffee leaf Search Trop Picture | |
| guarana Search Trop Picture | |
| kola nut Search Trop Picture | |
| lemon Search Trop Picture | |
| pomelo Search Trop Picture | |
| tea anther Search Trop Picture | |
| tea flower Search Trop Picture | |
| tea leaf Search Trop Picture | |
| tea pericarp Search Trop Picture | |
| tea seed Search Trop Picture | |
| tea seed coat Search Trop Picture | |
| tea stem Search Trop Picture |
Synonyms:
| 3,7- | dihydro-3,7-dimethyl-1H-purine-2,6-dione |
| 2,6- | dihydroxy-3,7-dimethyl purine |
| 2,6- | dihydroxy-3,7-dimethyl-purine |
| 2,6- | dihydroxy-3,7-dimethylpurine |
| 3,7- | dimethyl xanthine |
| 3,7- | dimethyl-1,3,7-trihydropurine-2,6-dione |
| 3,7- | dimethyl-2,3,6,7-tetrahydro-1H-purine-2,6-dione |
| 3,7- | dimethyl-3,7-dihydro-1H-purine-2,6-dione |
| 3,7- | dimethyl-xanthine |
| 3,7- | dimethylpurine-2,6-dione |
| 3,7- | dimethylxanthine |
| diuretin | |
| diurobromine | |
| 1H- | purine-2, 3,7-dihydro-3,7-dimethyl- |
| 1H- | purine-2,6-dione, 3,7-dihydro-3,7-dimethyl- |
| 1H- | purine-2,6-dione,3,7-dihydro-3,7- dimethyl- |
| teobromin | |
| theobromin | |
| theobromine natural | |
| theosalvose | |
| theostene | |
| thesodate | |
| xanthine, 3,7-dimethyl- |


